OLED Technology: What Is It and How Does It Work?
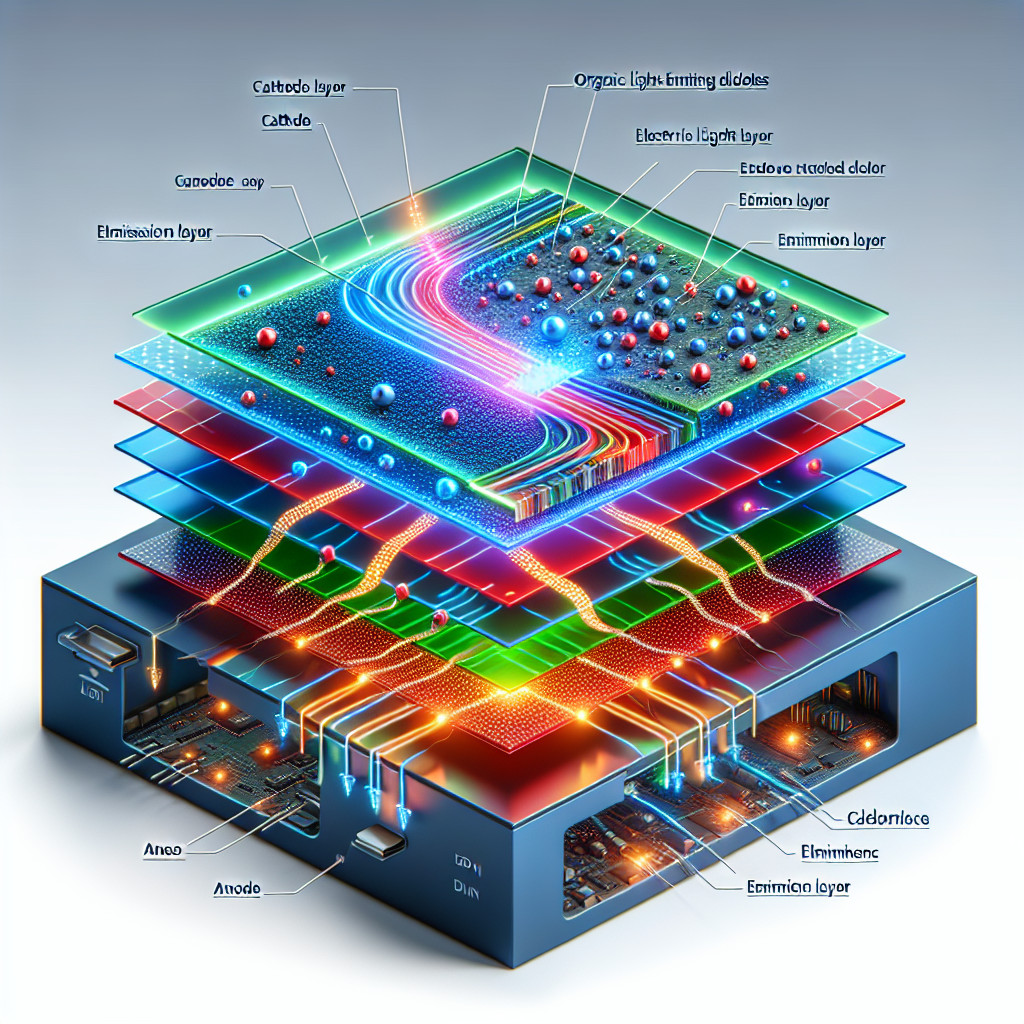
Organic Light Emitting Diode (OLED) technology is a revolutionary display technology that has been gaining traction in the consumer electronics market. OLEDs are thin, lightweight, and energy-efficient displays that offer superior image quality compared to traditional LCDs. OLEDs are made up of organic materials that emit light when an electric current is applied. This makes them ideal for use in displays, as they can be made very thin and can be used to create vibrant colors and deep blacks.
At the heart of OLED technology is the organic light-emitting diode (OLED). An OLED is a semiconductor device composed of two thin layers of organic material sandwiched between two electrodes. When an electric current is applied to the OLED, the organic material emits light. The color of the light depends on the type of organic material used. OLEDs are typically made from small molecules or polymers, which can be tailored to emit different colors of light.
The OLED structure is simple and efficient. The two electrodes are connected to a power source, and when a current is applied, the organic material emits light. This light is then directed towards the display, where it is used to create an image. OLEDs are also very efficient, as they require less power than traditional LCDs to produce the same amount of light.
OLEDs are used in a variety of applications, from smartphones and TVs to digital signage and automotive displays. OLEDs offer superior image quality compared to traditional LCDs, as they can produce deeper blacks and more vibrant colors. They are also thinner and lighter than LCDs, making them ideal for use in portable devices.
OLED technology is revolutionizing the display industry, and it is likely to become even more popular in the coming years. OLEDs offer superior image quality, thinner and lighter designs, and greater energy efficiency than traditional LCDs, making them an attractive option for a variety of applications.
OLED Technology: The Benefits and Drawbacks of Using OLED Displays
Organic Light-Emitting Diode (OLED) technology has become increasingly popular in recent years due to its superior performance compared to traditional display technologies. OLED displays offer a number of advantages, including improved image quality, higher contrast ratios, faster response times, and lower power consumption. However, OLED technology also has some drawbacks that should be considered before making a purchase.
One of the primary benefits of OLED technology is its superior image quality. OLED displays are capable of producing deeper blacks and brighter whites than traditional LCD displays, resulting in a higher contrast ratio. This improved contrast ratio allows for more vivid colors and greater detail in images. Additionally, OLED displays have faster response times than LCDs, which makes them ideal for applications that require quick response times, such as gaming and video editing.
Another advantage of OLED technology is its low power consumption. OLED displays require less power than LCDs, which makes them more energy efficient. This can be beneficial for applications that require long battery life, such as mobile devices. Additionally, OLED displays are thinner and lighter than LCDs, which makes them ideal for applications where size and weight are important factors.
Despite the many benefits of OLED technology, there are some drawbacks that should be considered. One of the primary drawbacks is the cost. OLED displays are more expensive than LCDs, which can make them prohibitively expensive for some applications. Additionally, OLED displays are more susceptible to burn-in than LCDs, which can be an issue for applications that require static images to be displayed for long periods of time. Finally, OLED displays are not as bright as LCDs, which can be an issue for applications that require a high level of brightness.
In conclusion, OLED technology offers a number of advantages over traditional LCD displays, including improved image quality, higher contrast ratios, faster response times, and lower power consumption. However, OLED technology also has some drawbacks, such as higher cost, susceptibility to burn-in, and lower brightness. Therefore, it is important to consider the benefits and drawbacks of OLED technology before making a purchase.
OLED Technology: Exploring the Latest Developments in OLED Technology and Its Applications
Organic Light Emitting Diode (OLED) technology is a rapidly developing field of research that has the potential to revolutionize the way we use and interact with displays. OLEDs are thin, lightweight, and energy-efficient, making them ideal for a variety of applications, from mobile phones and televisions to automotive displays and medical devices. In this article, we will explore the latest developments in OLED technology and its applications.
The most significant advancement in OLED technology is the development of flexible OLEDs. These displays are made from thin, flexible plastic substrates, allowing them to be bent and folded without damaging the display. This makes them ideal for use in wearable devices, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, as well as for curved displays in televisions and automotive dashboards. Additionally, flexible OLEDs are more durable than traditional displays, making them less prone to damage from drops and other impacts.
Another major development in OLED technology is the use of quantum dots. Quantum dots are tiny particles of semiconductor material that can be used to create displays with higher color accuracy and brightness than traditional OLEDs. This makes them ideal for use in high-end televisions and other displays that require accurate color reproduction. Additionally, quantum dots can be used to create displays with higher contrast ratios, making them ideal for use in virtual reality headsets and other applications that require a high level of detail.
Finally, OLED technology is being used in a variety of medical applications. OLEDs can be used to create displays that are thin, lightweight, and energy-efficient, making them ideal for use in medical devices such as endoscopes and other imaging systems. Additionally, OLEDs can be used to create displays that are highly visible in low-light conditions, making them ideal for use in medical devices that require accurate readings in dark environments.
In conclusion, OLED technology is a rapidly developing field of research that has the potential to revolutionize the way we use and interact with displays. The latest developments in OLED technology include the development of flexible OLEDs, the use of quantum dots, and the use of OLEDs in medical applications. As OLED technology continues to evolve, it is likely that we will see even more applications for this versatile technology in the future.